High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition where the force of blood against artery walls is consistently too high, usually defined as 130/80 mmHg or higher.
This condition often develops due to poor lifestyle choices such as a high-sodium diet, lack of physical activity, or excessive alcohol intake. Hypertension often presents no symptoms, making it a “silent killer” that can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure if left untreated.
Recommended Reading: Top 5 Early Signs Of Heart Failure In Women (Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment)
Top 5 Best Homemade Remedies For High Blood Pressure (For Instant Relief)

Table Of Contents
What is High Blood Pressure?
High BP
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition where the force of blood against artery walls is too high, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.

High blood pressure, also called hypertension, occurs when blood consistently pushes against artery walls with high force, typically 130/80 mmHg or more. It’s often a silent condition, so regular checkups are vital to prevent complications.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
Hypertension usually has no symptoms, but in some cases, it may cause headaches, dizziness, or chest pain. Risk factors include a poor diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and family history.
Stages Of High Blood Pressure
Stages Of High BP
The stages of high blood pressure range from elevated (slightly above normal) to stage 1 and stage 2 hypertension, with increasing severity and higher risks for heart issues.
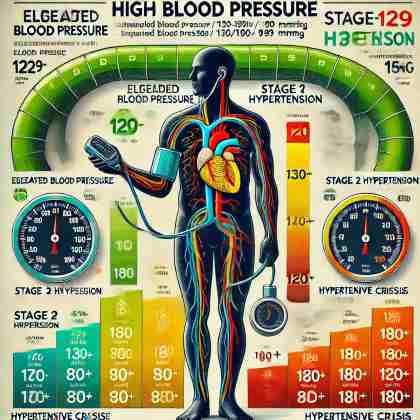
| Stage | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elevated Blood Pressure | 120-129 | Less than 80 | This is the pre-hypertensive stage, where the blood pressure is slightly higher than normal but not yet in the hypertensive range. It’s a warning sign to make lifestyle changes to avoid progressing to hypertension. |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 | Mild hypertension, where lifestyle changes and possibly medications are required to manage blood pressure. |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 or higher | 90 or higher | This is severe hypertension, needing medications and monitoring to avoid complications like heart disease or stroke. |
| Hypertensive Crisis | Higher than 180 | Higher than 120 | This is a medical emergency, requiring immediate attention to prevent life-threatening complications such as stroke or heart attack. |
Homemade Remedies For High Blood Pressure
Homemade Remedies For High BP
Homemade remedies for high blood pressure include stress management, reducing salt, regular exercise, and a healthy diet rich in potassium, all of which naturally support heart health and lower blood pressure.

| Remedy | How It Helps | How to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic Beverage | Limiting alcohol reduces strain on the heart and blood vessels. | Avoid excessive alcohol; stick to moderate consumption (1 drink/day for women, 2 drinks/day for men). |
| Stress Management | Reducing stress helps lower blood pressure spikes. | Practice yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or relaxation techniques. |
| Smoking Cessation | Quitting smoking improves heart health and lowers blood pressure. | Avoid tobacco products and seek support if needed to quit smoking. |
| Reduce Salt Intake | Less salt reduces fluid retention and lowers blood pressure. | Aim for less than 1,500 mg of sodium daily. |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and helps control blood pressure. | Engage in 30 minutes of moderate exercise like walking or biking, most days of the week. |
| Eat More Potassium | Potassium helps balance sodium levels, lowering blood pressure. | Include bananas, leafy greens, and potatoes in your diet. |
| Healthy Diet | Eating a balanced diet supports overall heart health. | Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Follow the DASH or Mediterranean diet. |
| Manage Weight | Losing excess weight helps reduce pressure on blood vessels. | Aim for gradual weight loss with balanced eating and regular exercise. |
| Sleep | Proper sleep lowers stress and regulates blood pressure. | Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. |
| Cut Back on Caffeine | Reducing caffeine intake can help lower blood pressure spikes. | Limit coffee, tea, and energy drinks. |
| Drink Water | Staying hydrated helps regulate blood pressure. | Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day. |
| Dark Chocolate | Flavonoids in dark chocolate help relax blood vessels. | Eat a small piece of dark chocolate (70% cocoa or higher) daily. |
| Avoid Too Much Sugar | Limiting sugar helps reduce weight and heart stress, lowering blood pressure. | Avoid sugary drinks, desserts, and snacks. |
| Herbal Supplements | Natural herbs like garlic and hibiscus help regulate blood pressure. | Consider supplements like garlic extract or hibiscus tea, but consult a doctor first. |
| Weight Loss | Shedding extra pounds can significantly reduce blood pressure. | Combine diet and exercise for gradual weight loss. |
| Can Medication Help? | Prescribed medications help manage hypertension if lifestyle changes aren’t enough. | Work with a healthcare professional to determine the right medication for you. |
| Eat Heart-Healthy Foods | Heart-friendly foods help keep blood vessels healthy and reduce pressure. | Focus on omega-3s (found in fish), fiber, and antioxidant-rich foods. |
| Garlic | Garlic dilates blood vessels, improving circulation and lowering blood pressure. | Consume raw garlic or garlic supplements daily. |
| Berries | Rich in antioxidants, berries support heart health and lower blood pressure. | Add berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries to your diet. |
| DASH Diet | The DASH diet emphasizes nutrient-rich foods that help lower blood pressure. | Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy while cutting back on salt and saturated fats. |
| Monitor Blood Pressure | Regular monitoring helps track progress and alert to any spikes in blood pressure. | Check your blood pressure at home regularly with a reliable monitor. |
| Reduce BP with Carrots | Carrots are rich in potassium and antioxidants that help lower blood pressure. | Eat raw carrots or drink carrot juice regularly. |
| Blueberry Juice | Blueberries are high in antioxidants, which can help lower blood pressure and improve heart health. | Drink blueberry juice or add blueberries to your diet regularly. |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Deep breathing relaxes the nervous system, lowering stress and blood pressure. | Practice slow, deep breathing for 5-10 minutes daily. |
Best Medicine For High Blood Pressure
Medicine For High BP
High blood pressure medications help relax blood vessels, reduce heart strain, and manage hypertension. Common types include beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics.
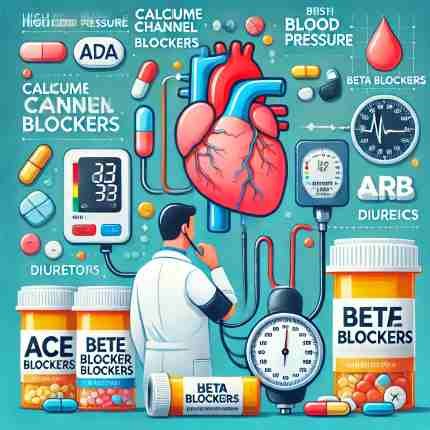
| Category | Common Drugs | How They Work | Uses | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs) | Amlodipine, Nifedipine, Verapamil, Diltiazem | Block calcium from entering heart and vessel muscles, relaxing them and lowering blood pressure | Treat high blood pressure, angina, heart rhythm disorders | Dizziness, leg swelling, constipation, headache |
| Diuretics (Water Pills) | Hydrochlorothiazide, Furosemide, Chlorthalidone | Help kidneys remove extra sodium and water, lowering blood volume and pressure | Effective for high blood pressure, heart failure, kidney disease | Increased urination, low potassium, dehydration, muscle cramps |
| ACE Inhibitors | Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril, Ramipril | Block enzyme that narrows blood vessels, relaxing them and lowering pressure | Treat high blood pressure, and heart failure, protect kidneys in diabetes | Cough, high potassium, low blood pressure, kidney issues |
| Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) | Losartan, Valsartan, Irbesartan | Block angiotensin II, allowing blood vessels to relax | Similar to ACE inhibitors, often used for high blood pressure, heart failure, kidney protection | Dizziness, high potassium, kidney problems |
| Beta Blockers | Atenolol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol | Block adrenaline effects, slow heart rate, reduce heart’s workload, and lower pressure | Treat high blood pressure, chest pain, heart failure, post-heart attack | Fatigue, cold extremities, slow heart rate, depression |
| Vasodilators | Hydralazine, Minoxidil | Directly relax blood vessel muscles, lowering blood pressure | Used for resistant hypertension or emergencies | Rapid heartbeat, fluid retention, headaches, dizziness |
| Alpha Blockers | Doxazosin, Prazosin, Terazosin | Block norepinephrine, relaxing blood vessels for better blood flow | Treat high blood pressure, enlarged prostate | Dizziness, headache, palpitations, fatigue |
| Centrally Acting Drugs | Clonidine, Methyldopa | Act on the brain to reduce signals that narrow blood vessels | For hard-to-control blood pressure | Drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, depression |
| Peripheral Adrenergic Inhibitors | Reserpine | Block nerve signals from the brain to blood vessels, reducing constriction | Less commonly used now due to side effects | Drowsiness, depression, nasal congestion |
| Renin Inhibitors | Aliskiren | Block renin, an enzyme that increases blood pressure | Used with other meds for high blood pressure | Diarrhea, high potassium, low blood pressure |
| Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRAs) | Spironolactone, Eplerenone | Block aldosterone, reducing water and salt retention, lowering blood pressure | Treat high blood pressure, heart failure | High potassium, breast tenderness, kidney issues |
| Chlorthalidone | Chlorthalidone | A long-acting diuretic that removes excess fluid to lower blood pressure | Commonly used in older adults for high blood pressure | Low potassium, dehydration, muscle cramps |
| Metolazone | Metolazone | Diuretic that helps reduce fluid, used for resistant hypertension, and kidney issues | Often combined with other diuretics for heart failure | Dizziness, dehydration, low electrolytes |
How To Lower Blood Pressure Instantly In An Emergency?
How to Lower BP Instantly
In an emergency, lowering blood pressure quickly can involve deep breathing, relaxing, and lying down while seeking immediate medical help for proper treatment.

| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing Exercise | Sit comfortably, close your eyes, and take slow, deep breaths. Inhale through your nose, hold briefly, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat until you feel calmer. Helps reduce stress and temporarily lower blood pressure. |
| Drink Water | Hydration is key to managing blood pressure. Drinking water can help regulate it by balancing fluids in the body. |
| Reduce Stress | Practice relaxation techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation to calm your mind and body. |
| Avoid Caffeine & Alcohol | Both substances can raise blood pressure temporarily, so it’s best to limit their intake during a spike. |
| Eat Potassium-Rich Foods | Foods like bananas, leafy greens, and potatoes can balance sodium levels and help manage blood pressure. |
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure
Natural ways to lower blood pressure include regular exercise, reducing salt intake, managing stress, and eating potassium-rich foods like bananas and leafy greens.

| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Manage Stress | Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation to reduce stress, which can lower blood pressure. |
| Quit Smoking | Smoking raises blood pressure. Quitting helps improve overall heart health and lowers blood pressure. |
| Limit Alcohol | Reducing alcohol intake helps control blood pressure. Stick to moderate levels to avoid spikes. |
| Exercise Regularly | Physical activity like walking, jogging, or swimming helps strengthen the heart and lower blood pressure. Aim for at least 30 minutes daily. |
| Eat a Healthy Diet | Focus on eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Include heart-healthy fats and limit processed foods. |
| Maintain a Healthy Weight | Weight loss, even as little as 10 pounds, can significantly lower blood pressure. |
| Reduce Salt (Sodium) | Too much salt increases blood pressure. Aim to limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day (preferably 1,500 mg). |
| Cut Back on Caffeine | Caffeine can temporarily spike blood pressure. Monitor your intake and reduce consumption if needed. |
| Get Enough Sleep | Lack of sleep can negatively affect blood pressure. Aim for 7-8 hours of good quality sleep each night. |
| Monitor Blood Pressure | Regularly checking your blood pressure helps you track progress and detect any concerning changes. |
| Eat Berries | Berries, especially blueberries, are rich in antioxidants that may improve heart health and help lower blood pressure. |
| Dark Chocolate | Small amounts of dark chocolate (at least 70% cocoa) can help reduce blood pressure thanks to its antioxidant content. |
| Increase Potassium Intake | Potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, and leafy greens help balance sodium levels, lowering blood pressure. |
| Include Whole Grains | Whole grains such as oats, brown rice, and quinoa can support heart health and lower blood pressure. |
| Eat Beets | Beets and beetroot juice have been shown to help lower blood pressure due to their high nitrate content. |
| Citrus Fruits | Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits are rich in vitamins and nutrients that promote healthy blood pressure. |
| Garlic | Garlic may help lower blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and improving blood flow. |
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Lifestyle Factors
- Unhealthy Diet (High Sodium, Low Potassium): A diet high in salt increases blood pressure, while low potassium intake fails to balance sodium’s effects.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Inactivity weakens the heart, making it work harder to pump blood, which raises blood pressure.
- Excessive Alcohol Intake: Drinking too much alcohol can damage the heart and increase blood pressure levels.
- Smoking: Smoking temporarily raises blood pressure and damages the arteries, leading to long-term hypertension.
- Being Overweight or Obese: Excess body weight forces the heart to work harder, raising blood pressure.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress can contribute to high blood pressure by triggering unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating or smoking.
- Poor Sleep: Inadequate or poor-quality sleep can lead to increased blood pressure, especially in people with sleep apnea.
Medical Conditions
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidneys struggle to regulate salt and water balance, leading to increased blood pressure.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of hypertension.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: This condition causes breathing interruptions during sleep, raising blood pressure levels.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both underactive and overactive thyroids can influence blood pressure.
- Adrenal Gland Disorders: Hormonal imbalances from adrenal issues can cause hypertension.
- Pregnancy Complications: Conditions like preeclampsia raise blood pressure during pregnancy.
Other Contributing Factors
- Family History of High Blood Pressure: Genetics play a role, and those with a family history are at higher risk.
- Age: Blood pressure tends to rise with age due to arterial stiffness.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, are at higher risk for developing hypertension.
- Certain Medications: Some medicines, such as birth control pills or decongestants, can raise blood pressure.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
Common Symptoms
- Headaches: Persistent or severe headaches can be a sign of elevated blood pressure.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or tightness in the chest may occur during high blood pressure episodes.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy can be linked to hypertension.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing might indicate blood pressure spikes.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some may feel nauseous or vomit during hypertensive episodes.
- Blurred Vision: Sudden or ongoing vision problems can be a result of high blood pressure.
- Nosebleeds: Frequent nosebleeds may occur in individuals with uncontrolled hypertension.
- Anxiety: Feeling unusually anxious can sometimes accompany elevated blood pressure.
- Pain: Pain spreading to the arm, neck, jaw, or back can be a sign of severe hypertension.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating with lightheadedness or nausea might signal a hypertensive crisis.
Severe Symptoms (Emergency)
- Chest Pain That Won’t Go Away: Seek help if chest pain persists and is accompanied by difficulty breathing or lightheadedness.
- Blood Pressure Higher Than 180/120 mmHg: This requires immediate medical attention.
- Numbness or Weakness: Sudden numbness or weakness in the limbs or face.
- Difficulty Speaking or Confusion: Sudden problems with speech or understanding can signal a hypertensive emergency.
Side Effects Of High Blood Pressure
Common Symptoms
- Headaches: Frequent or intense headaches can occur due to high blood pressure.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy is often linked to hypertension.
- Blurred Vision: Vision problems may develop as a result of increased pressure on blood vessels in the eyes.
- Nosebleeds: Repeated nosebleeds can be a sign of dangerously high blood pressure.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or tightness in the chest may indicate heart-related issues caused by hypertension.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing is a common symptom, especially during physical activity.
- Fatigue: Feeling exhausted could be related to high blood pressure.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea or even vomit in severe cases.
Serious Complications
- Heart Attack: Uncontrolled hypertension can damage the heart and increase the risk of heart attacks.
- Stroke: High blood pressure weakens blood vessels in the brain, leading to a higher chance of strokes.
- Kidney Damage: Hypertension can harm the kidneys, potentially causing kidney failure.
- Vision Loss: Over time, high blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems or blindness.
Organ Damage
- Heart: Increased risk of heart attacks, heart failure, and aortic dissection.
- Brain: High blood pressure can cause strokes and cognitive issues.
- Kidneys: Hypertension may lead to kidney damage or failure.
- Eyes: Retinal damage and vision loss are possible due to uncontrolled blood pressure.
Prevention Tips for High Blood Pressure
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy. Cut down on salt, processed foods, and foods high in saturated fats.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity, like walking or cycling, most days of the week.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to keep stress levels in check.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol: Smoking raises blood pressure and damages the heart. Limit alcohol intake to avoid increased pressure on your arteries.
Monitor Blood Pressure at Home
- Regular checks: Keep an eye on your blood pressure at home using a reliable monitor. This helps you notice changes early and adjust your habits or treatment if needed.
- Track your progress: Write down your readings to share with your doctor, allowing them to better manage your condition and make adjustments when necessary.
Benefits Of High Blood Pressure Medication
- Alpha-Blockers:
- How they work: Alpha-blockers help by relaxing blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily.
- Benefit: This reduces resistance in the arteries, lowering overall blood pressure and improving circulation.
- Centrally Acting Drugs:
- How they work: These medications send signals to the brain and nervous system to relax blood vessels.
- Benefit: By calming the nervous system, they help reduce stress on the heart and lower blood pressure.
- Vasodilators:
- How they work: Vasodilators directly relax the muscles in the walls of blood vessels.
- Benefit: This widens the blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow, which helps lower blood pressure.
Recommended Reading: Top 5 Early Signs Of Heart Failure In Women (Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment)
FAQs
How do alpha-blockers help with high blood pressure?
Alpha-blockers work by relaxing your blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through. This lowers your blood pressure and improves circulation.
What do centrally acting drugs do for high blood pressure?
Centrally acting drugs send signals to your brain to relax your blood vessels. This helps reduce stress on your heart and lowers your blood pressure.
How do vasodilators lower blood pressure?
Vasodilators directly relax the muscles in your blood vessel walls, allowing the vessels to widen. This reduces pressure, making it easier for blood to flow and lowering your blood pressure.
Why is it important to manage high blood pressure with medication?
Managing high blood pressure with medication helps lower the risk of serious health problems like heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. It helps keep blood pressure in a healthy range, protecting your overall health.
Can high blood pressure medication reduce the risk of heart disease?
Yes, blood pressure medication significantly lowers the risk of heart disease by keeping blood pressure under control and reducing the strain on your heart and blood vessels.
Should I combine lifestyle changes with high blood pressure medication?
Yes, combining medication with lifestyle changes like eating a healthy diet, exercising, reducing salt, and managing stress help improve the control of our blood pressure.
Are there side effects of taking high blood pressure medication?
Some medications may cause side effects like dizziness, fatigue, or headaches.
Are there any foods I should avoid while on high blood pressure medication?
You may need to avoid foods high in sodium and limit caffeine and alcohol. Certain medications may also interact with foods like grapefruit.
Conclusion
Summary of Remedies
In this article, we explored five natural remedies that may help reduce high blood pressure:
- Garlic: Known for relaxing blood vessels and improving circulation.
- Hibiscus Tea: A natural diuretic that helps reduce fluid buildup and pressure.
- Bananas: Rich in potassium, helping balance sodium levels and control pressure.
- Dark Chocolate: Contains flavonoids that improve blood flow and lower pressure.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Helps reduce stress, which can lower blood pressure.
Final Recommendations
These remedies offer natural ways to manage blood pressure, but they should be used alongside long-term lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, exercise, and regular medical checkups. Always consult your doctor before trying new remedies, especially if you are on medication for hypertension.
Disclaimer
Commissions we earn from partner links on this page do not influence our content. Our editorial content is based on thorough research and insights from qualified medical professionals to ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
Information provided on Doseway is for educational purposes only. Your health and wellness are unique to you, and the products and services we review may not be suitable for your circumstances. We do not offer personal medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment plans. For specific advice, please consult with a healthcare professional. Doseway adheres to strict editorial integrity standards. To the best of our knowledge, all content is accurate as of the date posted, though offers and information may change. The opinions expressed are the author’s own and have not been influenced, approved, or endorsed by our partners.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty
Add a Comment