Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It primarily affects the genital area but can also affect other parts of the body. Many people with genital herpes either have no symptoms or only mild ones, which makes it difficult to know when they are infected.
There are two types of HSV: HSV-1, which commonly causes cold sores but can also lead to genital infections, and HSV-2, which is more often responsible for genital herpes. While the condition is chronic, it can be managed effectively with antiviral treatments and lifestyle adjustments to reduce outbreaks and prevent transmission.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Keep Eating Food You’re Allergic To?
Home Remedies For Genital Herpes: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention

Table Of Contents
Recommended Reading: Top 5 Ways To Get Rid Of Allergies Permanently
What Is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is a common viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It affects the genital and surrounding areas, leading to sores or blisters that can be painful. Many people may not even know they have it because symptoms can be very mild or absent altogether.
Key Points
- Caused by HSV: There are two types of herpes viruses: HSV-1 (often causes cold sores) and HSV-2 (commonly responsible for genital herpes).
- Symptoms: Some people have no symptoms, while others may develop small, painful blisters that break open into sores.
- Transmission: It spreads through direct contact, often during sexual activity.
- Recurrent outbreaks: The virus stays in the body and can cause repeated episodes of sores or blisters, though these are often less severe than the first outbreak.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Cat Allergies Naturally: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Types Of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Type of HSV
There are two main types of herpes simplex virus (HSV): HSV-1, which typically causes oral herpes, and HSV-2, which usually leads to genital herpes.
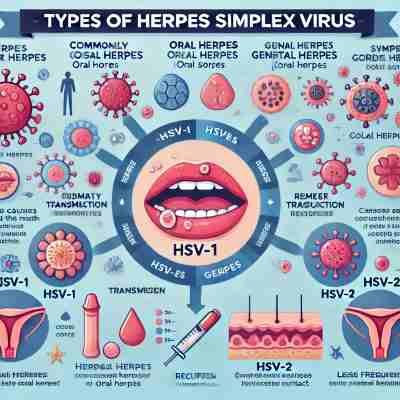
| Type of HSV | Primary Association | Transmission | Symptoms | Recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSV-1 | Commonly causes oral herpes (cold sores), but can also cause genital herpes | Spread through oral contact, but can also be transmitted to the genitals through oral-genital contact | Causes blisters or sores around the mouth (oral herpes) and can sometimes cause genital blisters | Less frequent recurrences compared to HSV-2 |
| HSV-2 | Most commonly associated with genital herpes | Spread through sexual contact (vaginal, anal, or oral sex) | Causes painful blisters or sores on the genitals, rectum, or mouth | More frequent recurrences, though they become less severe over time |
Recommended Reading: Best Allergy Medicine For Pet Allergies Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Stages of Genital Herpes
Stages Of HSV
Genital herpes progresses through stages, starting with tingling or itching, followed by the appearance of painful sores, and eventually healing after scabbing over.
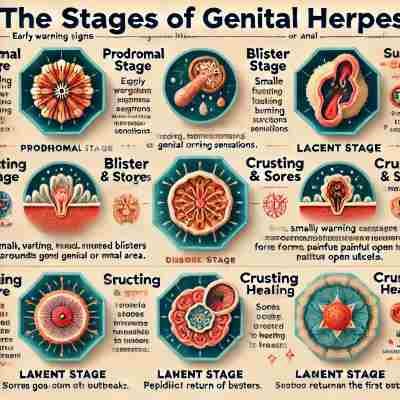
| Stage | Details | Symptoms | Causes/Triggers | Treatment/Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prodromal Stage | Early warning stage before visible symptoms appear. | Tingling, itching, or burning sensations in the genital area. | Often triggered by stress, illness, or other factors. | Antiviral medications can help reduce symptoms if taken early. |
| Blister Stage | Small blisters or red bumps form in the affected area. | Painful, fluid-filled blisters around the genitals or anus. | Virus replication causes the formation of blisters. | Keep the area clean and dry; use antiviral medications for symptom relief. |
| Rupture & Sores | Blisters break open, forming painful ulcers. | Open sores or ulcers that may ooze fluid and are highly painful. | The virus damages the skin, causing the blisters to rupture. | Pain management with topical creams and antiviral treatments. |
| Crusting & Healing | Sores dry out and begin to heal. | Sores crust over, scab, and heal within a few days to weeks. | Natural healing process the place as the virus goes dormant. | Allow the area to heal naturally; avoid touching sores to prevent infection. |
| Latent Stage | The virus goes dormant but stays in the body. | No visible symptoms, as the virus is inactive. | The virus hides in nerve cells until triggered by certain factors. | No specific treatment is needed during this stage, but antivirals can reduce recurrence. |
| Recurrent Outbreaks | Future outbreaks after the initial infection. | Recurrence of blisters and sores, though usually milder than the first outbreak. | Triggered by stress, fatigue, or other environmental factors. | Antiviral medications help shorten the duration and severity of outbreaks. |
Recommended Reading: Over-The-Counter Antihistamine For Hives (Causes And Symptoms)
Best Medical Treatment Options for Genital Herpes
Treatment Type
The best medical treatment for genital herpes includes antiviral medications like acyclovir and valacyclovir, which help reduce outbreak frequency and severity while managing symptoms effectively.
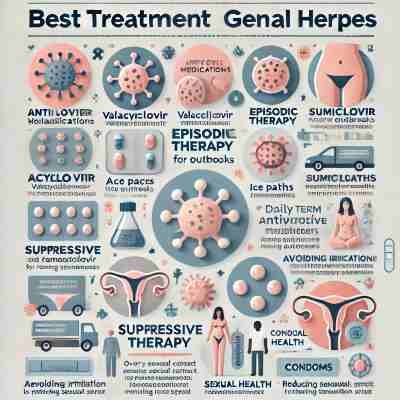
| Treatment Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | Antiviral drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are prescribed to manage outbreaks and reduce their frequency. |
| Episodic Therapy | Take antiviral meds during an outbreak to shorten its duration and ease symptoms. |
| Suppressive Therapy | Daily antiviral medication for people with frequent outbreaks minimizes recurrence and reduces the risk of spreading the virus. |
| Pain Relievers | Over-the-counter pain relief options like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain during outbreaks. |
| Home Remedies | Simple measures like using ice packs, warm baths, and wearing loose clothing can help relieve symptoms. |
| Avoiding Irritation | Wearing loose clothing and avoiding tight-fitting garments can reduce irritation around sores. |
| Hygiene Practices | Washing hands thoroughly after touching sores is important to avoid spreading the virus. |
| Sexual Health | Avoid sexual contact during outbreaks and inform sexual partners about your condition to prevent transmission. |
| Condom Use | Using condoms can reduce the risk of transmitting the herpes virus to your partner. |
Recommended Reading: Food Allergy Treatment At Home (Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment)
Causes of Genital Herpes
- Sexual Contact
- Vaginal, Anal, or Oral Sex: The most common cause of genital herpes. The virus spreads through direct contact during sexual activity.
- Close Genital Contact: Even without penetration, the virus can transmit through skin-to-skin contact between the genital areas.
- Kissing
- Oral Herpes Transmission: If a person with oral herpes (cold sores caused by HSV-1) kisses someone, they can spread the virus to the genitals, leading to genital herpes.
- Sharing Sex Toys
- Using sex toys without cleaning them properly can transmit the herpes virus between partners.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission
- During Childbirth: A pregnant woman with active genital herpes sores can pass the virus to her baby during delivery, which can lead to a serious condition called neonatal herpes.
- Touching Sores
- Touching an active herpes sore and then touching other areas, including the genitals, can spread the virus to different parts of the body.
- Asymptomatic Shedding
- Silent Transmission: The herpes virus can be spread even when no visible sores are present. This is called asymptomatic shedding, where the virus is still active on the skin.
- HSV-1 and HSV-2
- HSV-1: While mainly causing oral herpes, it can also spread to the genital area through oral-genital contact.
- HSV-2: This is the primary cause of genital herpes and is more commonly linked to genital infections.
- No Cure
- Lifelong Virus: Once infected, the herpes virus remains in the body permanently. While treatments can manage outbreaks, there is no cure.
- Recurring Outbreaks
- Reactivation of the Virus: The virus can cause repeated outbreaks, often triggered by stress, illness, or menstruation.
- Triggers for Outbreaks
- Common Triggers: Factors like emotional stress, weakened immune system, fatigue, or hormonal changes (e.g., during menstruation) can reactivate the virus, causing outbreaks.
- Prevention
- Condom Use: Using condoms during sexual activity can lower the risk of spreading the virus, but it doesn’t offer complete protection as the virus can still be transmitted through skin contact.
Recommended Reading: Is Hay Fever Contagious? Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
- Painful Blisters and Sores
- Small, fluid-filled blisters form around the genitals, anus, or mouth. These blisters break open and turn into painful sores.
- Itching or Tingling
- Before blisters appear, the affected area may feel itchy, tingly, or burning, signaling the start of an outbreak.
- Flu-Like Symptoms
- Fever, fatigue, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes often accompany the first outbreak, mimicking flu-like symptoms.
- Painful Urination
- Sores near the urinary tract can cause pain or a burning sensation when urinating.
- Unusual Discharge
- Some people, especially women, may notice unusual discharge from the vagina or urethra.
- Headaches
- Headaches are common during the initial outbreak as the body reacts to the virus.
- Muscle Aches
- General muscle aches and pains may occur, particularly during the first episode of infection.
- Sores that Scab and Heal
- Blisters eventually rupture, turn into sores, and scab over. The sores typically heal within 2 to 6 weeks.
- Recurring Outbreaks
- The virus remains in the body, and outbreaks can occur repeatedly. Recurring outbreaks are often less severe and shorter than the first.
- Mild or No Symptoms
- Many people may have very mild symptoms or no symptoms at all, which can make it hard to realize they have the virus.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
- During the first outbreak, the lymph nodes in the groin area may become swollen and tender.
- Important Information:
- Triggers for Recurrence: Stress, fatigue, or other illnesses can cause the virus to reactivate.
- Healing Time: Typically, blisters heal in 2 to 4 weeks during the first outbreak.
Recommended Reading: Natural Allergy Remedies For Eyes (Without Eye Drops)
Home Remedies for Genital Herpes
| Remedy | How to Use | Benefits | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | Take as directed by a doctor. Medications like acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir. | Reduces outbreak duration, severity, and transmission risk. | Nausea, headache, or dizziness may occur. |
| Pain Relief | Use over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen as per the package instructions. | Relieves pain and discomfort caused by sores. | Possible stomach upset or allergic reaction. |
| Topical Lidocaine | Apply lidocaine cream to the affected area as needed. | Numbs the area and reduces pain during outbreaks. | May cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. |
| Warm Baths | Soak in a warm bath for 10-20 minutes, optionally adding Epsom salts. | Soothes sore areas and speeds healing. | It can cause skin dryness if used excessively. |
| Cold Compresses | Apply a cold compress wrapped in a cloth to the sores for 10-20 minutes. | Reduces swelling, pain, and itching. | Overuse can cause skin irritation or frostbite. |
| Keep Sores Clean | Gently clean sores with mild soap and water, then pat dry. | Helps prevent infections and promotes faster healing. | Excessive cleaning can cause irritation. |
| Wear Loose Clothing | Wear loose-fitting cotton clothes, especially underwear, to reduce irritation. | Prevents friction and promotes the healing of sores. | None. |
| Avoid Touching Sores | Avoid direct contact with sores. If touched, wash hands thoroughly. | Prevent spreading the virus to other areas or people. | Risk of spreading infection if hygiene is not maintained. |
| Stress Management | Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing daily. | Reduces the frequency and severity of outbreaks triggered by stress. | None. |
| Suppressive Therapy | Take antiviral medication daily as directed by your doctor if you have frequent outbreaks. | Reduces the risk of outbreaks and transmission. | It may cause mild side effects like headaches or nausea. |
| Aloe Vera | Apply pure aloe vera gel to sores. | Soothes and speeds healing due to its natural anti-inflammatory properties. | Skin irritation may occur if sensitive to aloe vera. |
| Garlic | Eat raw garlic or take garlic supplements regularly. | Boosts immunity and has antiviral properties that may help fight infections. | It may cause an upset stomach or bad breath. |
| Tea Tree Oil | Dilute with a carrier oil (e.g., coconut oil) and apply to sores. | Reduces inflammation and promotes the healing of sores. | It can cause skin irritation if applied directly without dilution. |
| Honey | Apply raw honey to the sores as needed. | Soothes sores and promotes healing with its antibacterial and antiviral properties. | It may cause a sticky residue or skin irritation. |
| Dietary Adjustments | Increase lysine intake (found in yogurt, fish, and chicken) and reduce arginine (found in nuts, seeds). | Helps prevent herpes outbreaks by balancing amino acids in the body. | None if dietary changes are made in moderation. |
Recommended Reading: Best Medicine For Runny Nose And Sneezing (Causes And Treatment)
Antiviral Medications for Genital Herpes
| Medication | How to Use | Benefits | Uses | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acyclovir (Zovirax) | Oral tablets, cream, or liquid form. Take as prescribed by your doctor. | Reduces pain, speeds up healing, and decreases outbreak severity. | Used for initial, recurrent, and suppressive treatment of herpes. | Nausea, diarrhea, headache, or fatigue. |
| Famciclovir (Famvir) | Oral tablets. Take at the first sign of symptoms for best results. | Prevents virus replication, reduces the frequency of outbreaks. | Commonly used for recurrent episodes of genital herpes. | Headache, nausea, and possible skin rash. |
| Valacyclovir (Valtrex) | Oral tablets. Take as prescribed, ideally within 48 hours of symptoms. | Shortens the duration of outbreaks, helps sores heal faster. | Treats recurrent episodes and helps suppress frequent outbreaks. | Dizziness, nausea, abdominal pain, or vomiting. |
| Docosanol (Abreva) | Topical cream. Apply directly to sores as soon as symptoms appear. | Helps speed up healing and reduce viral activity on the skin. | Used to treat cold sores and minor genital herpes symptoms. | Localized skin irritation or dryness. |
| Penciclovir (Denavir) | Topical cream. Apply to affected areas every 2 hours while awake. | Relieves pain and discomfort, helps heal sores faster. | Mainly used for cold sores but also treats genital herpes lesions. | Mild stinging or burning at the application site. |
| Acyclovir Cream | Apply directly to the sores several times a day as prescribed. | Reduces pain and speeds up healing for mild outbreaks. | For treating sores during mild outbreaks, but not as effective as oral treatment. | Skin irritation, itching, or redness. |
| Pain Relievers (e.g., Ibuprofen) | Take orally as needed for pain management. | Helps relieve pain and reduce swelling during outbreaks. | Supports antiviral medications by alleviating pain symptoms. | Stomach upset, dizziness, or allergic reaction. |
| Topical Anesthetics (e.g., Lidocaine) | Apply to sores for temporary pain relief. | Provides temporary numbing to relieve pain from blisters. | Used alongside antiviral medications to relieve discomfort. | Skin irritation or allergic reaction. |
Recommended Reading: Allergy Medicine For Kids: Types, Uses, And Side Effects
Genital Herpes in Women {Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment}
Genital Herpes in Females
Genital herpes in women causes painful blisters or sores in the genital area, often accompanied by itching, burning, and flu-like symptoms during outbreaks. It can be managed with antiviral treatments.

Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It leads to painful blisters or sores around the genital area, anus, or mouth. While some women may not show any symptoms, others experience discomfort and flu-like symptoms.
Causes of Genital Herpes
- Sexual Contact: Herpes spreads primarily through skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- No Visible Symptoms: The virus can still spread even when there are no visible sores or symptoms.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes in Women
| Symptom | Details |
|---|---|
| Blisters and Sores | Small, painful blisters on the genitals that can burst and ooze. |
| Itching and Burning | Sensation of itching, burning, or tingling around the genital area. |
| Flu-like Symptoms | Fever, body aches, and fatigue, especially during the first outbreak. |
| Painful Urination | Discomfort or pain while urinating. |
| Swollen Glands | Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area. |
| Vaginal Discharge | Changes in vaginal discharge, which may become unusual during an outbreak. |
How Genital Herpes Spreads
- Skin-to-skin contact: The virus is spread through intimate contact with an infected person, especially during sexual activities.
- Even Without Symptoms: Herpes can still spread even if there are no visible sores or symptoms.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider examines any visible sores or symptoms.
- Lab Tests: A sample from a sore may be taken for laboratory testing to confirm herpes.
Treatment Options
| Treatment | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | These help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks, speeding up recovery. |
| Pain Relievers | Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help ease pain during outbreaks. |
| Daily Suppressive Therapy | Taking antiviral medication daily helps lower the frequency of outbreaks and reduces the risk of spreading the virus. |
Side Effects of Antiviral Medications
| Common Side Effects | Details |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Feeling of sickness in the stomach, which can occur with medication. |
| Headache | Mild to moderate headaches are common during antiviral treatment. |
| Dizziness | Some people may experience lightheadedness or dizziness. |
| Skin Irritation | Topical treatments can cause mild irritation or redness on the skin. |
Prevention Tips
- Use Condoms: Helps reduce the risk of transmission during sexual activity.
- Avoid Contact During Outbreaks: Avoid sexual activity during an outbreak to prevent spreading the virus.
- Open Communication: Inform your partner about the infection and take preventive steps together.
Recommended Reading: Allergy Medicine Dogs: Best Allergy Medicine For Dogs Licking Paws
Genital Herpes in Men {Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment}
Genital Herpes in Men
Genital herpes in men leads to painful sores or blisters around the genital area, often accompanied by itching, discomfort, and flu-like symptoms. Antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks and reduce transmission.

Genital herpes in men is caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 or HSV-2) and results in painful blisters and sores on the genitals, anus, or thighs. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact and can be present even when no visible sores are present.
Causes of Genital Herpes
- Sexual Contact: Herpes is spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person.
- No Visible Symptoms Needed: The virus can spread even when there are no visible sores.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes in Men
| Symptom | Details |
|---|---|
| Blisters and Sores | Painful blisters or sores on the genitals, thighs, or anus. |
| Pain and Itching | Discomfort, itching, or tingling around the affected areas. |
| Painful Urination | Burning or pain while urinating due to irritation of the urethra. |
| Flu-like Symptoms | Fever, body aches, and headaches during the initial outbreak. |
| Swollen Lymph Nodes | Swelling of lymph nodes in the groin area, especially during the first outbreak. |
| Discharge | Some men may experience discharge from the urethra. |
| Recurring Outbreaks | After the initial outbreak, herpes can return with shorter and less severe symptoms. |
How Genital Herpes Spreads?
- Sexual Contact: Spread through skin-to-skin contact during sex, even if sores are not visible.
- No Symptoms Needed: Herpes can spread even if the infected person has no active symptoms or sores.
Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
- Physical Exam: A doctor will look for visible sores or blisters on the genitals.
- Lab Tests: Samples from sores may be taken for lab testing to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
| Treatment | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | Help reduce the severity of outbreaks and lower the risk of spreading the virus. |
| Pain Relief | Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort during outbreaks. |
| Suppressive Therapy | Daily antiviral medication to reduce the frequency and severity of future outbreaks. |
Side Effects of Antiviral Medications
| Common Side Effects | Details |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Mild nausea or upset stomach. |
| Headache | Mild to moderate headaches during medication use. |
| Dizziness | Feeling lightheaded or dizzy as a side effect. |
| Skin Irritation | Possible skin irritation from topical treatments. |
Prevention Tips
- Use Condoms: Reducing the risk of transmitting herpes during sex.
- Avoid Sexual Activity During Outbreaks: Avoid sex when sores or other symptoms are present to reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
- Open Communication: Talk to your partner about STIs and take precautions together.
Side Effects of Genital Herpes
- Painful Blisters and Sores
- Small, painful blisters or sores appear around the genitals, buttocks, or thighs. These sores may break open and cause discomfort.
- Flu-Like Symptoms
- Fever, body aches, headaches, and fatigue are common during the first outbreak, similar to flu symptoms.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
- The lymph nodes, particularly in the groin area, may become swollen and tender.
- Itching, Tingling, or Burning
- Before blisters form, many people experience a tingling, itching, or burning sensation in the genital area.
- Painful Urination
- Sores in the genital area can make urination painful as urine passes over the blisters.
- Recurrent Outbreaks
- After the first infection, the virus stays in the body and can cause recurring outbreaks, though these are usually milder than the initial one.
- Increased Risk of HIV Infection
- Open sores from genital herpes can make it easier for HIV to enter the body, increasing the risk of contracting HIV.
- Newborn Infection
- If a pregnant woman has genital herpes, the virus can be passed to the baby during childbirth, leading to serious health issues for the newborn.
- Rare Complications
- In some cases, genital herpes can cause complications like eye infections (herpes keratitis), or brain inflammation such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- Psychological Impact
- Living with genital herpes can cause emotional stress, anxiety, and even depression due to the possibility of recurring outbreaks.
- Skin Irritation
- Blisters and sores can lead to irritation and discomfort in the surrounding skin, which may take time to heal.
- Fatigue
- Many people feel extremely tired during an outbreak, particularly during the first episode.
Prevention of Genital Herpes
- Condom Use
- Use condoms during all types of sexual activity (vaginal, anal, and oral) to lower the risk of transmission.
- Note: Condoms do not provide full protection, as herpes can spread through skin-to-skin contact outside the condom-covered area.
- Avoiding Sexual Contact During Outbreaks
- Avoid sex when visible sores or symptoms are present. The virus is most contagious during an active outbreak.
- Wait until the sores heal before resuming sexual activity to help prevent passing the virus to a partner.
- Open Communication with Partners
- Be honest with your sexual partners about your condition. Inform them if you have genital herpes so they can make informed decisions.
- Discuss prevention methods, such as condom use and antiviral treatments, to help reduce the risk of spreading the infection.
- Regular STI Testing
- Get regular tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) to monitor your sexual health.
- Especially important if you or your partner have multiple partners or engage in high-risk sexual behaviors. Early detection helps prevent the spread of herpes and other infections.
- Antiviral Medication
- Take antiviral medications like acyclovir or valacyclovir if prescribed by your doctor. These medicines can help lower the risk of outbreaks and transmission to your partner.
- Daily suppressive therapy may also reduce the chance of passing the virus.
- Good Hygiene Practices
- Wash hands thoroughly after touching sores or applying any medication to the affected area.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors that could spread the virus to others.
- Limit Sexual Partners
- Limit the number of sexual partners to reduce the risk of coming into contact with someone who might be infected.
- Use protection consistently with all partners, even in long-term relationships, if one partner is infected.
- Avoid Kissing and Oral Contact During Outbreaks
- Do not engage in kissing or oral sex when symptoms of oral herpes (cold sores) are visible, as it can spread to the genitals and other areas.
Recommended Reading: OTC Antihistamine For Hives
FAQs
What is genital herpes?
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is commonly spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. HSV-1 usually causes oral herpes (cold sores), but it can also cause genital herpes, while HSV-2 primarily causes genital infections.
What are the symptoms of genital herpes?
The most common symptoms include small, painful blisters or sores on the genitals, anus, or thighs. Some people experience itching, burning during urination, swollen lymph nodes, and flu-like symptoms such as fever or body aches. After the initial outbreak, recurrences can happen, though they tend to be less severe.
How is genital herpes transmitted?
Herpes spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can happen during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Even if visible sores are not present, the virus can still be passed to a partner.
Can genital herpes be cured?
There is no cure for genital herpes, but it can be managed. Antiviral medications like acyclovir or valacyclovir help reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks and lower the risk of spreading the virus to others.
How can I prevent transmitting genital herpes to my partner?
To reduce transmission risk, use condoms during all sexual activities. Avoid sexual contact during outbreaks when sores are present. Taking daily antiviral medication can also reduce the likelihood of spreading the virus.
What should I do if I think I have genital herpes?
If you notice symptoms of genital herpes, such as sores, itching, or burning during urination, see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Early treatment with antiviral medications can help reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
How are outbreaks managed?
Outbreaks can be managed with antiviral medications taken either during an outbreak (episodic treatment) or daily to prevent frequent outbreaks (suppressive therapy). Over-the-counter pain relievers, ice packs, and wearing loose clothing can help ease discomfort during outbreaks.
Is regular STI testing important?
Yes, regular testing for sexually transmitted infections is crucial, especially if you have multiple partners or engage in high-risk sexual behavior. Testing helps in early detection and treatment, preventing the spread of infections.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Keep Eating Food You’re Allergic To?
Conclusion
Managing genital herpes requires a combination of treatments and preventive actions. While there is no cure, antiviral medications, home care, and open communication with partners can help control outbreaks and reduce transmission risks.
Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. By practicing safe sex, maintaining good hygiene, and taking prescribed medication, individuals can minimize the impact of genital herpes on their daily lives. Staying informed and taking proactive steps toward prevention is key to managing the condition effectively.
Disclaimer
The commissions we earn from partner links on this page do not influence our content. Our editorial content is based on thorough research and insights from qualified medical professionals to ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
The information provided on Doseway is for educational purposes only. Your health and wellness are unique to you, and the products and services we review may not be suitable for your circumstances. We do not offer personal medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment plans. For specific advice, please consult with a healthcare professional. Doseway adheres to strict editorial integrity standards. To the best of our knowledge, all content is accurate as of the date posted, though offers and information may change. The opinions expressed are the author’s own and have not been influenced, approved, or endorsed by our partners.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty
Add a Comment