Eye socket pain, also called orbital pain, refers to discomfort or pain felt around or behind the eye. This pain can have multiple causes, including migraines, sinus infections, eye strain, and dental problems. Sometimes, it can also be linked to more serious conditions like glaucoma or optic neuritis.
Understanding the possible causes is important for finding the right treatment. Preventive measures like limiting screen time, managing allergies, and getting regular eye check-ups can help reduce the risk of eye socket pain.
Recommended Reading: 10 Best Period Pain Relief Pills (To Stop Period Pain Immediately)
Eye Socket Pain Causes, Prevention, & Treatment (Eye Socket Pain & Headache)

Table Of Contents
Recommended Reading: How To Control Period Pain? (10 Ways To Control Menstrual Cramps)
What is Eye Socket Pain? | Eye Socket Pain & Headache
Eye Socket Pain & Headache
Eye socket pain is discomfort behind or around the eye, often linked to headaches. Causes include sinus infections, migraines, eye strain, dental issues, injuries, glaucoma, and cluster headaches. The pain may be temporary or persistent, requiring proper diagnosis for effective relief.
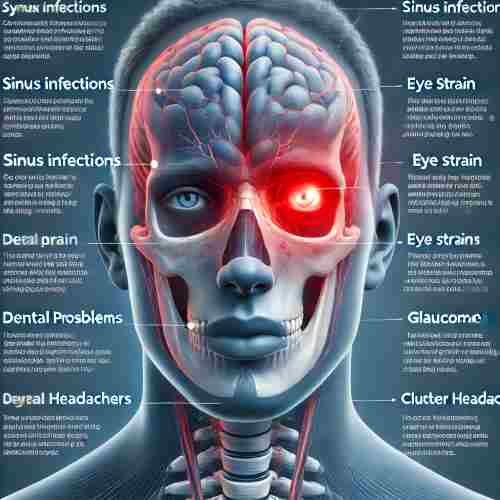
Eye socket pain refers to discomfort or aching around or behind the eye. It can feel like pressure, throbbing, or sharp pain. Often, this pain is linked to headaches, and you might feel both symptoms at the same time.
Common causes include sinus infections, migraines, eye strain, or even more serious issues like glaucoma. The pain can last a short time or be ongoing, depending on the cause. Understanding the reason behind the pain is important for proper treatment and relief.
Recommended Reading: Teenage Period Pain Relief Home Remedies (Top 10 Remedies)
Causes of Eye Socket Pain
- Sinusitis: Sinus infections or allergies can cause inflammation in the sinus cavities, leading to pressure and pain around the eyes.
- Migraines: Severe headaches, like migraines, often cause intense pain behind the eyes.
- Eyestrain: Long hours of screen use, poor lighting, or uncorrected vision can cause eye fatigue and pain in the eye socket area.
- Dental Problems: Issues with upper teeth can sometimes cause pain that spreads to the eye socket.
- Eye Injuries: Physical injuries to the eye can cause swelling and pain in and around the eye socket.
- Glaucoma: This condition increases pressure inside the eye, leading to significant discomfort or pain behind the eye.
- Cluster Headaches: These are intense headaches often centered around one eye, causing severe pain in the area.
Prevention Strategies for Eye Socket Pain
Prevention Strategies for Eye Socket Pain
Reduce screen time, manage stress, and stay hydrated to prevent eye socket pain. Treat allergies, get regular eye checkups, and maintain good sleep habits. For relief, use OTC painkillers, warm or cold compresses, artificial tears, or nasal sprays. Managing migraines can also help.

- Limit Screen Time: Reduce your screen usage and take frequent breaks to rest your eyes.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing activities like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to relax both your mind and body.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, as dehydration can worsen headaches and eye discomfort.
- Treat Allergies: Use antihistamines to manage allergies, and avoid triggers that may cause sinus inflammation.
- Regular Eye Checkups: Visit an eye doctor regularly to ensure your vision is healthy and corrected, preventing strain.
- Practice Good Sleep Habits: Ensure a consistent sleep routine, as poor sleep can increase headaches and eye-related pain.
Treatment Options for Eye Socket Pain
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Common painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to reduce eye socket pain.
- Warm or Cold Compresses: For sinus-related pain, applying a warm compress can help ease discomfort, while cold compresses are useful for reducing swelling from eye injuries.
- Artificial Tears: Eye drops can provide relief for dry eyes, which may help reduce irritation and pain around the eyes.
- Nasal Sprays: Decongestant nasal sprays can relieve sinus congestion, easing pressure and pain around the eye socket.
- Migraine Management: Identifying migraine triggers and taking preventive medication can help control migraines and related eye pain.
Recommended Reading: Top 10 Ways To Control Menstrual Cramps
Medicine for Eye Socket Pain
Medicine for Eye Socket Pain
OTC medications like ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetaminophen help relieve eye socket pain. Consult a doctor before use, especially if you have other conditions. Treating the root cause, such as sinus infections or eye strain, is essential. Anti-inflammatory eye drops may be prescribed if needed.

For eye socket pain, over-the-counter (OTC) medications like ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen, or acetaminophen (Tylenol) are commonly recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
Key Points About Eye Socket Pain Medication
Consult a Doctor First
Always speak with a doctor before taking any medication, especially if you have other medical conditions or are on other prescriptions.
Treating the Cause
To manage eye socket pain effectively, focus on addressing the root cause, such as eye strain or sinus infections.
Pain Relief Options
- OTC Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen, naproxen, acetaminophen.
- Eye Drops: Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory eye drops depending on the cause of the pain.
When to See a Doctor for Eye Socket Pain
- Severe or Persistent Pain: If your pain doesn’t improve with home treatments or worsens, it’s important to see a doctor.
- Vision Changes: Sudden changes in vision like blurriness or double vision need immediate medical attention.
- Swelling, Redness, or Discharge: These symptoms, especially with a fever, may point to an infection and require a doctor’s consultation.
- Recent Eye Injury: If you’ve had a recent eye injury causing pain, it’s crucial to seek medical care to prevent complications.
Indications & Uses
Indications & Uses
Eye socket pain relief is recommended for those with sinusitis, migraines, eye strain, or minor injuries. OTC pain relievers like ibuprofen help, along with warm compresses for sinus pain or cold compresses for swelling. Relief usually starts within 30–60 minutes, with compresses offering immediate comfort.

Who Should Use It?
This treatment is recommended for people experiencing eye socket pain caused by conditions such as sinusitis, migraines, eye strain, or minor eye injuries. It can also help those with general discomfort or tension headaches related to stress or overuse of digital devices.
Specific Conditions or Symptoms
- Sinus infections
- Migraines or tension headaches
- Eye strain from screens or poor lighting
- Dry eyes or inflammation
- Mild eye injuries or trauma
How to Use?
- Dosage Instructions: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen should be taken as directed on the label.
- Application Guidelines: If using compresses, apply a warm compress for sinus-related pain or a cold compress for injury-related swelling.
- Frequency of Use: Pain relievers can be taken as needed, but it’s important to not exceed the recommended dosage. Compresses can be applied for 10-15 minutes, a few times a day.
Effectiveness
Clinical Evidence
Over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) and acetaminophen have been proven effective in reducing pain and inflammation. Clinical studies support their use for headaches and sinus-related discomfort, though more severe causes of pain may require prescription medications.
Personal Experiences or Testimonials
Many people report relief from eye socket pain through a combination of rest, pain relievers, and compresses. Artificial tears are also widely praised for relieving dry, irritated eyes.
Expected Results
- Timeframe: Relief from pain typically occurs within 30 minutes to an hour after taking pain relievers. Eye drops or compresses can provide immediate comfort.
- Typical Outcomes: Users often experience reduced pain, less swelling, and relief from headaches or sinus pressure.
Side Effects & Precautions
Side Effects & Precautions
Eye socket pain treatments may cause mild stomach upset, dry eyes, or redness. Serious reactions like swelling or persistent redness need medical attention. OTC medications provide quick relief, but overuse can lead to side effects or dependency.

Common Side Effects
- Mild stomach upset from NSAIDs
- Dry eyes (if using eye drops too frequently)
- Temporary redness or irritation from compresses
Serious Side Effects
- Allergic reactions (swelling, rash, or breathing difficulty)
- Prolonged eye redness or swelling
- Severe headache that doesn’t improve with medication
When to Seek Medical Attention
If pain worsens or is accompanied by vision changes, severe swelling, or discharge, contact a doctor immediately. Seek help if you experience serious side effects from medications or eye treatments.
Precautions
- Avoid using NSAIDs if you have a history of ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Don’t overuse decongestants or eye drops, as this can worsen symptoms over time.
- Always consult a doctor if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications, as interactions could occur.
Pros & Cons of Treatment Approaches
Pros
- Quick Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen offer fast pain relief.
- Non-Invasive Relief: Warm or cold compresses can ease pain without the need for medication.
- Soothes Dry Eyes: Artificial tears help reduce dryness and discomfort, improving eye comfort.
Cons
- Temporary Relief: Some treatments only address the symptoms, not the root cause of the pain.
- Side Effects: Overusing decongestants or pain relievers may lead to unwanted side effects, like dependency or worsening symptoms over time.
Recommended Reading: Teenage Period Pain Relief Home Remedies
FAQs
What causes eye socket pain?
Eye socket pain can be caused by various factors such as sinus infections, migraines, eye strain, dental problems, or injuries. The exact cause depends on the symptoms and accompanying conditions.
How can I relieve eye socket pain at home?
For mild pain, you can try using over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, warm or cold compresses, and artificial tears. Resting your eyes and limiting screen time can also help.
When should I see a doctor for eye socket pain?
If the pain is severe, lasts longer than a few days, or is accompanied by vision changes, redness, or swelling.
Can stress cause pain behind the eyes?
Yes, stress can lead to tension headaches or migraines, which may cause pain behind or around the eyes. Relaxation techniques and stress management can help.
Can sinusitis cause pain around the eyes?
Yes, sinusitis can cause inflammation and pressure in the sinus cavities, which often leads to pain around the eyes and forehead. Treating the sinus infection usually relieves the pain.
Conclusion
Recommended Reading: Period Pain Relief Home Remedies
Summary of Causes and Treatment
Eye socket pain can result from various causes like sinusitis, migraines, or eye strain. Each cause requires specific treatment, such as medications, compresses, or preventive steps.
Final Recommendation
For mild discomfort, home remedies like warm or cold compresses and eye drops can provide quick relief. However, if the pain gets worse or doesn’t improve, it’s important to seek medical advice.
Who Should Seek Treatment
Anyone with severe or long-lasting pain, sudden vision changes, or eye injuries should consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Disclaimer
Commissions we earn from partner links on this page do not influence our content. Our editorial content is based on thorough research and insights from qualified medical professionals to ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
Information provided on Doseway is for educational purposes only. Your health and wellness are unique to you, and the products and services we review may not be suitable for your circumstances. We do not offer personal medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment plans. For specific advice, please consult with a healthcare professional. Doseway adheres to strict editorial integrity standards. To the best of our knowledge, all content is accurate as of the date posted, though offers and information may change. The opinions expressed are the author’s own and have not been influenced, approved, or endorsed by our partners.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty
Add a Comment