Wound Healing is a natural process where thebody repairs damaged skin or tissue after an injury. Wounds can be caused by accidents, surgeries, or other incidents, and they vary in severity. Antibiotics play a crucial role in helping the body fight infections that might occur in open or deep wounds.
In some cases, wounds can become infected, delaying the healing process. To support Wound Healing and prevent complications, antibiotic tablets are often prescribed. These medicines help toeliminate bacteria, reduce inflammation, and ensure a quicker recovery.
- Recommended Reading: Top 5 Antibiotics For Ear Piercing Infection (Infected Ear Piercing)
- Recommended Readings: Best Antibiotics For Acne And Pimples
Top 5 Best Antibiotic Tablets For Wound Healing {Treatments, And Medications}

Table Of Contents
Recommended Reading: Top 5 Best Antibiotics For Chest Infection (Fast Recovery)
What is a Wound?
Wound
A wound is any break or damage to the skin or tissue, caused by cuts, scrapes, burns, or other injuries, disrupting the body’s protective barrier.
A wound is any damage or break in the skin or underlying tissues. It can happen due to accidents, injuries, surgeries, or health conditions. Wounds are classified as either open (where the skin is broken) or closed (where the skin remains intact but tissues underneath are damaged).
Healing wounds quickly is important to prevent infections and other complications. Proper care ensures faster recovery and reduces the risk of more serious issues.
Why Are Antibiotics Important for Wound Healing?
Antibiotics play a key role in wound healing by helping to prevent and treat bacterial infections. When bacteria enter a wound, they can cause infections that slow down the healing process or lead to serious complications.
- How Antibiotics Work:
- Kill bacteria or stop their growth.
- Allow the body to focus on healing without the interference of infections.
Using antibiotics properly helps wounds heal faster and reduces the risk of severe health issues caused by infections.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotics For Intestinal Bacterial Infection (Stop Vomiting And Diarrhea)
Types of Wounds
Wound Types
Wounds can be classified as open (like cuts or burns) or closed (such as bruises), depending on whether the skin is broken or intact.
| Wound Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Avulsion | Severe injury where skin or tissue is forcibly torn away, often requiring surgical intervention. |
| Laceration | Deep cuts or tears in the skin caused by sharp objects, can range from minor to severe, often requiring stitches. |
| Surgical Wounds | Clean, intentional cuts made during surgeries for medical purposes, typically well-managed and monitored for healing. |
| Abrasion | Superficial scrapes on the skin, caused by friction against rough surfaces, affect the outer layer of the skin. |
| Puncture Wounds | Deep, narrow wounds caused by sharp objects like nails or needles, with a high risk of infection. |
| Diabetic Foot Ulcer | Chronic, slow-healing wounds on the feet, are common in people with diabetes due to poor circulation and nerve damage. |
| Traumatic Wounds | Injuries caused by accidents or violent incidents, including cuts, bruises, and fractures, often require urgent care. |
| Burns | Damage caused by heat, chemicals, or electricity; categorized by degrees (1st, 2nd, 3rd) depending on the severity of skin and tissue damage. |
| Pressure Ulcer | Also known as bedsores, caused by prolonged pressure on the skin, typically in bedridden patients, leading to tissue damage. |
| Venous Ulcer | Sores develop due to poor circulation in the veins, often occurring on the legs, and can be slow to heal. |
| Arterial Insufficiency Ulcer | Caused by poor blood flow in the arteries, leading to tissue damage, commonly affecting the legs or feet. |
| Open Wounds | Wounds where the skin is broken, exposing underlying tissues; examples include abrasions, lacerations, and puncture wounds. |
| Incision | Clean, precise cuts made by surgical instruments, often closed with stitches or staples. |
| Skin Tearing | Tears in the skin caused by shearing or trauma, are common in elderly individuals with fragile skin. |
| Acute Wounds | Short-term wounds that heal within a predictable timeframe, are typically caused by surgery or trauma. |
| Chronic Wounds | Wounds that take a long time to heal, are often due to underlying conditions like diabetes or poor blood circulation. |
| Malignant Wounds | Wounds caused by cancerous growths breaking through the skin are often difficult to manage. |
| Amputation | Surgical removal of a limb due to severe injury, infection, or other medical conditions. |
| Bruise | A closed wound where blood vessels under the skin are damaged, causing discoloration without breaking the skin. |
| Clean Wound | A wound with minimal contamination, usually caused by surgical procedures, and less likely to get infected. |
| Electrical Injuries | Damage is caused by exposure to electrical currents, which can result in both external burns and internal tissue damage. |
Recommended Reading: Best Vegan Brain Supplements (For Brain Health)
What is Wound Healing?
Wound Healing
Wound healing is the body’s natural process of repairing damaged skin or tissues after injury, involving stages like clotting, tissue repair, and regeneration.
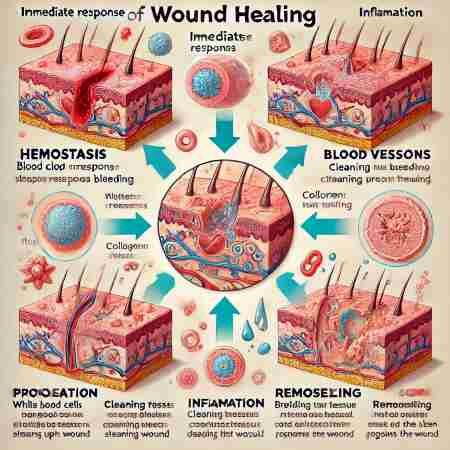
Wound healing is the body’s natural process of repairing damaged skin or tissues. It begins immediately after an injury and involves several complex steps that restore the skin’s structure and function. Proper wound healing is crucial to prevent infections and ensure that the skin regains its strength and flexibility.
Stages of Wound Healing
The wound healing process occurs in four main stages, each playing a critical role:
- Hemostasis (Immediate Response)
- When it happens: Right after an injury
- What happens: Blood vessels constrict to stop bleeding, and blood clots form to seal the wound.
- Why it’s important: This prevents excessive blood loss and protects the wound from infection.
- Inflammation (Cleaning the Wound)
- When it happens: 1–3 days after injury
- What happens: Blood vessels widen (vasodilation), and immune cells like white blood cells arrive at the wound site. These cells clean up damaged tissue and fight off infections.
- Why it’s important: Inflammation helps to clear the wound and prepare it for new tissue growth.
- Proliferation (Building New Tissue)
- When it happens: 4–21 days after injury
- What happens: New tissue, blood vessels, and collagen start to grow. The wound begins to shrink as it heals.
- Why it’s important: This stage rebuilds the damaged area and closes the wound.
- Remodeling (Strengthening the Wound)
- When it happens: 21 days to 1 year after injury
- What happens: The wound matures, and scar tissue forms. This scar tissue may not be as strong or flexible as the original skin but helps to close the wound permanently.
- Why it’s important: Remodeling strengthens the healed tissue and restores skin integrity.
Key Points to Remember
- Hemostasis: Blood clots stop bleeding right after injury.
- Inflammation: Immune cells clean the wound and fight infections.
- Proliferation: New tissue forms, closing the wound.
- Remodeling: The wound matures, and scar tissue develops.
Recommended Readings: Antibiotics For Skin Rashes And Itching | Strongest Allergy Medicine
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on wounds, slowing healing.
- Poor Nutrition: Lack of nutrients hinders the body’s ability to repair tissue.
- Age: Older age slows down the healing process due to reduced cell regeneration.
- Pharmaceutical Drugs: Some medications, like steroids, can impair wound healing.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels interfere with circulation, delaying healing.
- Infection: Bacteria in the wound can cause inflammation and slow recovery.
- Wound Care: Proper care, like keeping the wound clean and moist, promotes healing.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases like heart disease and poor circulation slow down the healing process.
- Protein-Energy Malnutrition: Insufficient protein and calories affect tissue repair.
- Stress: High-stress levels can weaken the immune system, slowing healing.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol intake disrupts healing by affecting the immune system.
- Blood Supply: Poor blood circulation reduces oxygen flow to the wound, delaying healing.
- Moisture: Maintaining a moist environment aids faster healing by promoting tissue regeneration.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces oxygen supply, leading to slower healing.
- Foreign Body: Objects like splinters or dirt in the wound can delay recovery.
- Ischemia: Lack of blood flow to the wound can prevent healing.
- Repeated Trauma: Constant injury to the same area can prevent the wound from closing.
- Immunodeficiency: A weakened immune system slows down the body’s healing response.
- Necrosis: Dead tissue at the wound site must be removed to allow healing.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Poor vein function in the legs can slow wound healing, especially for leg ulcers.
Principles of Wound Management
Principles of Wound Healing Management
The principles of wound management focus on cleaning, protecting, and promoting healing by preventing infection and supporting tissue repair.
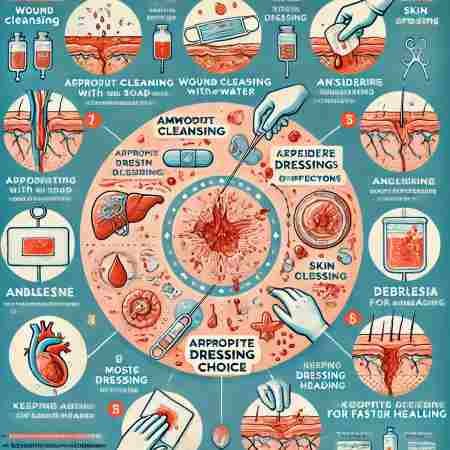
- Wound Cleansing: Clean the wound with soap and water to remove dirt, and debris, and reduce infection risk.
- Antibiotics: Consider antibiotics if there are signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus.
- Analgesia: Provide pain relief (analgesia) to ensure the patient is comfortable during treatment.
- Appropriate Dressing Choice: Choose the right dressing for the wound type (e.g., moist dressing for faster healing) and change it regularly.
- Debridement: Remove dead tissue (debridement) from the wound to promote healthy tissue growth and prevent infection.
- Skin Closure: For open wounds, consider stitches, staples, or adhesives to close the wound, promoting faster healing.
- Wound Assessment: Assess the wound frequently to monitor progress and detect any complications early.
- Acute Wounds: Treat acute wounds immediately with the right approach to prevent complications.
- Dressing and Follow-up: Keep the wound dressed appropriately and schedule follow-up to check the healing progress.
- Hemostasis: Stop bleeding using gentle pressure or bandages to achieve hemostasis.
- Keep the Wound Moist: Maintain a moist wound environment to accelerate healing and reduce scarring.
Recommended Readings: Bacterial Infection In Anus Treatment | Fistula Treatment
Five Basic Wound Healing Principles
- Assessment: Evaluate the patient’s overall health and factors that could slow healing.
- Cleaning: Clean the wound carefully with water and mild soap.
- Dressing: Use the appropriate dressing and change it regularly.
- Antibiotics: Prescribe antibiotics if infection is suspected.
- Follow-up: Monitor the wound for signs of healing or complications.
Additional Tips
- Apply gentle pressure to stop bleeding.
- Run cool water over burn wounds.
- Avoid popping blisters.
- Reduce swelling with compression bandages or socks.
- Encourage physical activity to boost circulation and healing.
Recommended Readings: Best Antibiotics For Acne And Pimples
Treatment of Wound Healing
Treatment of Wound
Wound healing treatment involves cleaning, dressing, managing pain, and sometimes using antibiotics or surgery to support proper recovery.
Wound healing treatments are based on the type and severity of the wound. Key methods include cleaning, dressing, pain relief, and sometimes surgery.
Cleaning the Wound
- Gently wash the wound with soap and water or saline solution.
- Remove any dirt and debris.
- Apply pressure to stop bleeding.
Dressing
- Cover the wound with a sterile bandage or dressing.
- Change the bandage daily or when it becomes wet or dirty.
- Use an absorbent dressing for wounds with heavy drainage.
Pain Medication
- Take acetaminophen (Tylenol) for pain relief.
- Avoid aspirin, as it can prolong bleeding.
Surgery
- Large wounds may require stitches or staples.
- Remove dead tissue or explore deep wounds if necessary.
- Vascular surgery may be done to improve blood supply to aid healing.
Other Treatments
- Get a tetanus shot if the wound is at risk of infection.
- Use antibiotics or antimicrobial dressings if there are signs of infection.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may help increase oxygen in the blood for better healing.
Home Remedies
- Apply honey, propolis, or coconut oil to aid healing.
- Use garlic on minor wounds for its antibacterial properties.
Wound Cleansing
- Use water or saline to clean the wound, removing debris and bacteria to prevent infection.
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are critical for treating infected wounds, especially if signs of infection like swelling or redness appear.
Wound Dressings
- Use appropriate dressings depending on the wound type. Keeping the wound moist promotes faster healing.
Debridement
- Removing dead or damaged tissue helps the Wound heal properly and prevents infections.
Skin Closure
- Sutures or staples may be needed for deep wounds to ensure proper closure and healing.
Recommended Readings: The Counter Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
List Of Best Antibiotic Tablets for Wound Healing
List Of Best Antibiotic Tablets
Here are some of the best antibiotic tablets for wound healing, including Amoxicillin-Clavulanate, Cephalexin, and Clindamycin, commonly used for infection control and faster recovery.

| Antibiotic | Overview | Mechanism | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanate | Treats mild to moderate infections. | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. | Effective for skin and soft tissue infections. | Nausea, diarrhea, allergic reactions. |
| Cephalexin | Common for skin infections like cellulitis. | Disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis. | Good for various skin infections and wound healing. | Stomach upset, rash, diarrhea. |
| Clindamycin | Used for skin infections when allergic to penicillin. | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. | Effective against skin and soft tissue infections. | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, colitis. |
| Doxycycline | Broad-spectrum antibiotic. | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. | Effective against resistant bacteria, used for Wound Healing infections. | Nausea, sun sensitivity, esophagitis. |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole | Combination antibiotic for bacterial infections, including MRSA. | Inhibits bacterial folic acid synthesis. | Effective for resistant strains like MRSA. | Rash, nausea, increased sensitivity to sunlight. |
| Dicloxacillin | Used for skin and soft tissue infections. | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. | Treats minor infections and Wound Healing infections. | Stomach upset, rash. |
| Minocycline | Treats a variety of infections, including skin infections. | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. | Useful for wound healing and skin infections. | Dizziness, nausea, tooth discoloration. |
| Linezolid | Often used for drug-resistant bacterial infections. | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. | Effective for resistant bacteria like MRSA. | Diarrhea, headache, bone marrow suppression. |
| Vancomycin | A strong antibiotic for serious infections. | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. | Effective against severe infections like MRSA. | Kidney damage, low blood pressure. |
| Daptomycin | Used for complicated skin infections and resistant bacteria. | Disrupts bacterial membrane function. | Effective for Wound Healing infections caused by resistant bacteria. | Muscle pain, elevated liver enzymes. |
| Telavancin | Used for complicated skin and soft tissue infections. | Disrupts bacterial cell membrane. | Effective for treating serious bacterial infections. | Kidney damage, taste disturbances. |
| Levofloxacin | Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used for wound infections. | Inhibits bacterial DNA replication. | Effective for treating wounds, especially freshwater injuries. | Nausea, diarrhea, tendon rupture. |
| Ceftazidime | Used for serious infections, especially for burns and wounds. | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. | Commonly used in hospitals for wound care. | Diarrhea, rash, injection site reactions. |
| Fluoroquinolones | Treats wounds from saltwater injuries. | Inhibits bacterial DNA replication. | Good for wound infections involving water exposure. | Tendon rupture, nervous system effects. |
| Ciprofloxacin | Used for wounds from freshwater environments. | Inhibits bacterial DNA replication. | Highly effective for freshwater-related Wound Healing infections. | Nausea, diarrhea, tendon rupture. |
Recommended Readings: Best Antibiotic For Breast Infection | Breast Infection Treatment
Best Antibiotic For Wound Infection In Child
Best Antibiotic For Child
The best antibiotics for wound infections in children include Amoxicillin-Clavulanate, Cephalexin, and Clindamycin, commonly used to treat skin and soft tissue infections.

| Antibiotic Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanate | Treats mild to moderate infections, including wounds. |
| Cephalexin | Effective for treating skin and soft tissue infections. |
| Clindamycin | Commonly used for skin and soft tissue infections, especially abscesses. |
| Doxycycline | Helps treat skin infections and soft tissue wounds. |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole | Effective against skin and wound infections caused by bacteria. |
| Dicloxacillin | Used for treating mild to moderate bacterial infections. |
| Cefprozil | Used for treating bacterial infections, especially in skin wounds. |
| Cefuroxime Axetil | Treats a variety of bacterial infections, including skin wounds. |
| Cefadroxil | Commonly used to treat skin and soft tissue infections. |
| Minocycline | Treats skin and soft tissue infections, including wounds. |
| Linezolid | Used for more serious or drug-resistant wound infections. |
Injectable Antibiotics For Severe Wound Infections
- Vancomycin, Daptomycin, and Telavancin are used for more severe wound infections that require hospital treatment.
When to Use Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are prescribed to treat bacterial infections in wounds. If a wound shows signs of infection such as redness, swelling, pus, or warmth, antibiotics may be needed to prevent complications.
Recommended Readings: Antibiotics For Stomach Infection | Antibiotics For Gastroenteritis
Best Antibiotic For Wound Infection In Adults
Best Antibiotic For Adults
For adults, common antibiotics for wound infections include Amoxicillin-Clavulanate, Cephalexin, and Clindamycin, effective in treating skin and soft tissue infections.

| Antibiotic Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanate (Augmentin) | Treats mild to moderate infections, including wounds. |
| Cephalexin | Cephalosporin is effective for skin and soft tissue infections. |
| Clindamycin | Used for treating skin and soft tissue infections, especially abscesses. |
| Doxycycline | Treats skin infections in patients allergic to penicillin. |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole | Commonly used for wound infections in patients allergic to penicillin. |
| Penicillin V | Treats mild to moderate bacterial infections, including wounds. |
| Dicloxacillin | Effective for treating skin and wound infections caused by bacteria. |
| Minocycline | Used for treating skin and soft tissue infections. |
| Linezolid | For serious or drug-resistant wound infections. |
| Vancomycin | Treats severe wound infections, often used in hospitals. |
| Daptomycin | Effective for complicated skin infections and severe wound cases. |
| Telavancin | Used for serious bacterial wound infections that require hospital care. |
Recommended Readings: Best Antibiotics For Vaginal Infection | Vaginal Itching
Best Oral Antibiotics for Wound Healing
| Antibiotic Name | Use |
|---|---|
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanate (Augmentin) | Effective for treating mild to moderate infections, including puncture wounds. |
| Cephalexin | Commonly used for skin and soft tissue infections. |
| Clindamycin | Treats skin infections, particularly in cases resistant to other antibiotics. |
| Dicloxacillin | Used for treating bacterial skin and wound infections. |
| Doxycycline | Ideal for patients allergic to penicillin, effective for soft tissue infections. |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole | Useful for skin infections, particularly in penicillin-allergic patients. |
| Fluoroquinolones | Used for patients with allergies to penicillin. |
| Minocycline | Effective for soft tissue infections. |
| Linezolid | Treats serious and resistant wound infections. |
| Penicillin V | Commonly used for mild to moderate skin and wound infections. |
| Vancomycin | Often reserved for severe or hospital-treated infections. |
How They Are Used?
Dosage: Based on the patient’s health and infection type.
Treatment Duration: Usually 5-10 days for mild to moderate infections, but this varies with severity and patient response.
Other Antibiotics for Wound Healing
- Mupirocin, Neomycin, Bacitracin: Topical antibiotics that treat minor skin infections.
- Polymyxin, Tetracycline: Useful for treating superficial infections and wound healing.
Additional Medications for Wound Healing
- Topical Antibiotics: Bacitracin and Neomycin for superficial infections.
- Antiseptics: Such as Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide for cleaning wounds.
- Collagenase Ointments: Helps remove dead tissue and promotes healing.
- Growth Factor Gels: Boosts tissue repair and wound closure.
- Corticosteroids: Reduces excessive inflammation but should be used cautiously.
Recommended Readings: The Counter Antibiotics For Tooth Infection
Wound Healing Therapies
| Therapy | Details |
|---|---|
| Cold Compression Therapy | Reduces swelling and pain by applying cold to the wound. |
| Debridement | Removal of dead or damaged tissue to promote healing. |
| Hyperbaric Medicine | Uses high-pressure oxygen to speed up healing, especially for chronic wounds. |
| Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy | Uses suction to remove excess fluid and promote tissue growth. |
| Antibiotics | Prevents or treats infection in the wound. |
| Electrical Muscle Stimulation | Stimulates muscles to increase blood flow and support healing. |
| Skin Grafting | Transplanting healthy skin to cover large wounds. |
| Skin Substitutes | Artificial or biological materials are used to cover wounds and promote healing. |
| Wound Contraction | Gradual shrinking of the wound as tissues pull together during healing. |
Recommended Readings: Antibiotics For UTI | Antibiotics For UTI In Men+Women
Best Home Remedies for Wound Healing
Best Home Remedies
Natural remedies like honey, aloe vera, and turmeric can help speed up wound healing by reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair.

| Remedy | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Honey | Natural antibacterial properties speed up healing. |
| Garlic | Contains allicin, which has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Turmeric | Anti-inflammatory helps prevent infection. |
| Coconut Oil | Moisturizes and protects the wound. |
| Lavender | Soothes irritation has mild antiseptic properties. |
| Apple Cider Vinegar | Antimicrobials can clean wounds when diluted. |
| Calendula | Promotes tissue regeneration and reduces inflammation. |
| Chamomile | Soothes the skin and reduces irritation. |
| Cinnamon | Antimicrobial properties help fight infections. |
| Clove | Natural antiseptic reduces pain and cleanses the wound. |
| Cucumbers | Hydrates and reduces swelling. |
| Onion | Contains compounds that reduce infection and inflammation. |
| Aloe Vera | Soothes and promotes faster healing. |
| Tea Tree Oil | Antibacterial, needs to be diluted with carrier oil. |
| Essential Oils | Various oils can reduce pain and promote healing. |
Types of Wound Dressings
| Dressing Type | Usage and Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hydrocolloid Dressing | Maintains a moist environment, ideal for minor burns, abrasions, and slow-healing wounds. |
| Alginate Dressing | Highly absorbent, used for wounds with heavy exudate (fluid). |
| Foam Dressings | Absorbs excess fluid, protects the wound, and keeps the area moist. |
| Gauze | Basic dressing is used for cleaning, covering, and absorbing fluids from wounds. |
| Hydrogels | Provides moisture, helps with dry or painful wounds, and promotes tissue growth. |
| Composites | Multi-layer dressings that offer a combination of absorption, adhesion, and protection. |
| Collagen | Helps speed up tissue repair by providing a natural protein structure for the wound. |
| Transparent Film | Protects the wound while allowing the skin to breathe and monitoring the healing process. |
| Antimicrobial Dressing | Releases antimicrobial agents to prevent or treat infections. |
| Biologic Dressings | Made from natural or bioengineered materials, often used for severe burns or chronic wounds. |
| Hydrofibers | Absorbs heavy wound fluid and forms a gel-like covering for better healing. |
| Non-Adherent Dressings | Does not stick to the wound, making it easier to remove without disturbing healing. |
| Silver Dressings | Contains silver, which has antimicrobial properties to prevent infection. |
| Deodorizing Dressings | Controls odor from wounds, ideal for infected or highly exuding wounds. |
| Hydroconductive Dressings | Draws out fluid from the wound, helping manage exudate and keeping the area clean. |
How to Use These Remedies
- Aloe Vera: Apply a thin layer of gel directly on the wound to soothe and reduce inflammation.
- Turmeric: Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste and apply to the wound to prevent infection.
- Tea Tree Oil: Dilute with carrier oil (like coconut oil) and apply to the wound to fight bacteria.
- Garlic: Apply fresh garlic to the wound for 10-20 minutes for its antimicrobial effects.
- Chamomile: Use as a compress or brew tea to soothe skin irritation and reduce swelling.
Signs of Good Wound Healing
- Scabbing: A protective layer forms over the wound, shielding it from bacteria.
- Mild Swelling: Some swelling is normal in the first few days as the body reacts to the injury.
- Tissue Growth: The edges of the wound begin to close as new tissue forms.
- Decreasing Pain: As the wound heals, discomfort should gradually lessen.
- Minimal Drainage: A small amount of clear or yellow fluid is normal; this helps clean the wound.
- Pink or Red Tissue: This is called granulation tissue, and it’s a good sign that the wound is healing well.
Causes of Delayed Wound Healing
- Poor Circulation:
- Conditions like varicose veins or swelling can limit blood flow to the wound, making it harder for the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients needed for healing.
- Infection:
- Bacterial infection is one of the main causes of delayed healing. Bacteria can enter the wound, causing inflammation, swelling, and further damage.
- Medical Conditions:
- Chronic health issues such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking weaken the immune system and impair the body’s ability to repair itself.
- Age & Stress:
- Older individuals naturally heal more slowly due to reduced cell regeneration, while stress weakens the immune response, also slowing the healing process.
- Other Contributing Factors:
- Repeated trauma, poor nutrition, and inadequate wound care (such as not keeping the wound clean or moist) can prevent proper healing and extend recovery time.
Recommended Readings: Best Antibiotics For Strep Throat | Strep Throat Antibiotics
FAQs
What are oral antibiotics for wound healing?
Oral antibiotics are medicines you take by mouth to treat infections in wounds. They work by killing or stopping the growth of bacteria that cause infections in cuts, punctures, or surgical wounds.
When should I use antibiotics for a wound?
You should use antibiotics if a wound shows signs of infection, like redness, swelling, warmth, pain, or pus. If the wound is large, deep, or doesn’t heal on its own, antibiotics may help.
How long do I need to take antibiotics for a wound infection?
Most wound infections are treated with antibiotics for 5-10 days, depending on the severity.
What are common antibiotics for wound healing?
Some commonly used antibiotics include Amoxicillin-Clavulanate, Cephalexin, Clindamycin, and Doxycycline. These are effective against different types of bacteria that can cause wound infections.
Can I use antibiotics if I’m allergic to penicillin?
Yes, if you’re allergic to penicillin, alternatives like Doxycycline or Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole are often prescribed.
Are there any side effects of taking antibiotics for wound infections?
Common side effects may include nausea, diarrhea, stomach upset, or rashes. If you experience severe side effects like difficulty breathing or swelling.
Do antibiotics help all types of wounds?
No, antibiotics are only needed for wounds with bacterial infections. Minor wounds without infection usually heal on their own without the need for antibiotics.
Can I clean my wound while taking antibiotics?
Yes, cleaning your wound with mild soap and water is important, even when taking antibiotics. Keep the wound clean to prevent further infection and help the healing process.
Should I cover my wound while on antibiotics?
Yes, covering the wound with a sterile bandage can help protect it from further contamination and promote healing. Change the bandage regularly as recommended.
How do antibiotics help wounds heal faster?
Antibiotics fight the bacteria causing the infection, reducing inflammation and pus, which allows the wound to heal more effectively. However, antibiotics do not directly speed up tissue repair.
Recommended Reading: Best Antibiotics For Infected Ear Piercing
Conclusion
Antibiotics play a vital role in treating and preventing infections in wounds, especially those at risk of bacterial contamination. Using the right antibiotic is important for effective healing, based on the type and severity of the wound. This helps fight infections and speeds up recovery.
Proper wound care goes beyond antibiotics. It includes cleaning the wound, using appropriate dressings, and seeking timely medical help. This ensures that the wound heals well and lowers the risk of complications. By following these steps, you can promote faster recovery and better overall wound health.
Disclaimer
Commissions we earn from partner links on this page do not influence our content. Our editorial content is based on thorough research and insights from qualified medical professionals to ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
Information provided on Doseway is for educational purposes only. Your health and wellness are unique to you, and the products and services we review may not be suitable for your circumstances. We do not offer personal medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment plans. For specific advice, please consult with a healthcare professional. Doseway adheres to strict editorial integrity standards. To the best of our knowledge, all content is accurate as of the date posted, though offers and information may change. The opinions expressed are the author’s own and have not been influenced, approved, or endorsed by our partners.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty
Add a Comment